Documentation
/ Methodological guide
: 
Analysis of variance or ANOVA (Analyse de variance): decomposition of the variance (as a breakdown) to elementary pieces (also know as HDMR, Hoeffding's decomposition, Sobol's decomposition... c.f. Section V.1.1.3).
Cumulative distribution function or CDF
(Fonction de répartition): function of a real-valued random variable 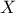 which, once evaluated at
which, once evaluated at 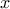 , gives the probability that
, gives the probability that 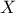 will take a value less than or equal to
will take a value less than or equal to 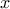 (c.f. Section II.1.1).
(c.f. Section II.1.1).
Kriging or Gaussian process (Krigeage ou processus gaussien): is a family of interpolation methods that uses information about the "spatial" correlation between observations to make predictions with a confidence interval at new locations (c.f. Section IV.5).
Latin hypercube sampling or LHS (Échantillonage par hypercube latin): sampling methods that stratifies the probability space by dividing it in equal probabilities (c.f. Section III.2.1).
Leave-one-out or LOO (validation croisée un contre tous): type of cross-validation for which a surrogate model is re-train on the learning database removing just one point, in order to obtain an estimation of this new model on this precise point (c.f. Section IV.1.2).
Likelihood (vraisemblance): is the hypothetical probability that an event that has already occurred would yield a specific outcome. The concept differs from that of a probability in that a probability refers to the occurrence of future events, while a likelihood refers to past events with known outcomes [Likeli].
Low discrepancy sequence: (Suite à faible discrépance):
sequence for which the discrepancy is low, meaning the proportion of points in the sequence falling into an arbitrary set
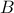 is close to proportional to the
measure of
is close to proportional to the
measure of 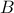 (c.f. Section III.3).
(c.f. Section III.3).
Pareto front (front de Pareto): a set of nondominated solutions, being chosen as optimal, if no objective can be improved without sacrificing at least one other objective (c.f. Section VI.1.2).
Pearson coefficient (Coefficient de Pearson): it is the linear correlation coefficient (c.f. Section V.1.1.2).
Principal component analysis or PCA (Analyse en conclusion principale): the process of computing the principal components and using them to perform a change of basis on the data, sometimes using only the first few principal components and ignoring the rest (c.f. Section II.3).
Probability density function or PDF (Densité de probabilité): function whose value at any given sample (or point) in the sample space (the set of possible values taken by the random variable) can be interpreted as providing a relative likelihood that the value of the random variable would equal that sample (c.f. Section II.1.1).
Quantile (Quantile): the quantile 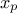 , for a probability
, for a probability 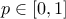 , is the lowest value of a random variable
, is the lowest value of a random variable 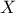 so that
so that 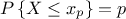 (c.f. Section II.2.4).
(c.f. Section II.2.4).
Screening method (méthode de criblage): process that extracts, isolates and identifies a compound or group of components in a sample with the minimum number of steps and the least manipulation of the sample (c.f. Chapter V).
Simple random sampling or SRS (Échantillonage simple aléatoire): independent generation of samples following provided PDFs (c.f. Section III.2.1).
Sparse grids: numerical techniques to represent, integrate or interpolate high dimensional functions.