Documentation
/ User's manual in Python
: 
This method is called when instead of having a list of input parameters (in terms of stochastic distribution) that one
would like to transform into a design-of-experiments, the user has a dataset, made out of a very large number of points. In this case,
it is possible, using the TNeuralGas class, to create sub-sample of points that would be
representative of the complete provided-set, based on a NeuralGas algorithm. This might be useful in order to test the
output of long and complicated codes or computations without leaving aside a possible area of the input parameter
values.
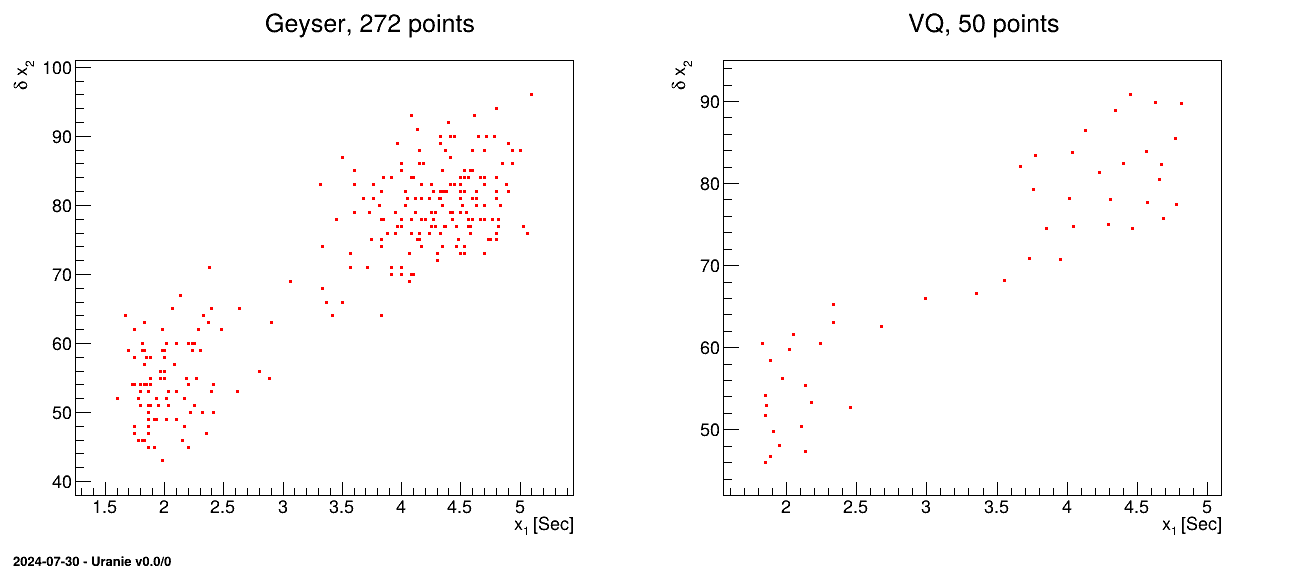
Figure III.16 shows the effect of the reduction of the sample in the simple case of a
two-dimensional plane, when considering the "geyser.dat" file and its sub-sample of 50 points.
Figure III.16. Example of a dataset reduction (the geyser one) using the NeuralGas algorithm, to go from 272 points (left) to 50 one (right)
 |
Here is an example of how to use the neuralgas algorithm to reduce a database.
c = ROOT.TCanvas("Can", "Can", 10, 32, 1300, 600)  c.Divide(2, 1)
tdsGeyser = DataServer.TDataServer("tdsgeyser", "Neural Gas for Geyser")
tdsGeyser.fileDataRead("geyser.dat")
tvq = Sampler.TNeuralGas(tdsGeyser, "", 50)
c.Divide(2, 1)
tdsGeyser = DataServer.TDataServer("tdsgeyser", "Neural Gas for Geyser")
tdsGeyser.fileDataRead("geyser.dat")
tvq = Sampler.TNeuralGas(tdsGeyser, "", 50) 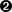 tvq.setDrawProgressBar(False)
tdsng = tvq.getSubSample("loop=20")
tvq.setDrawProgressBar(False)
tdsng = tvq.getSubSample("loop=20")  c.cd(1)
tdsGeyser.draw("x2:x1")
ROOT.gPad.GetPrimitive("__tdshisto__0").SetTitle("Geyser, 272 points")
c.cd(1)
tdsGeyser.draw("x2:x1")
ROOT.gPad.GetPrimitive("__tdshisto__0").SetTitle("Geyser, 272 points")  c.cd(2)
tdsng.draw("x2:x1")
ROOT.gPad.GetPrimitive("__tdshisto__0").SetTitle("VQ, 50 points")
c.cd(2)
tdsng.draw("x2:x1")
ROOT.gPad.GetPrimitive("__tdshisto__0").SetTitle("VQ, 50 points")
Construction of the plot
Creation of | |
Construction of the neuralgas object from the provided database | |
Get the sub-sample as a new dataserver, after looping 20 the algorithm | |
Access the latest histogram drawn on current pad, to change its title |